Measuring the operating parameters of a circuit is essential to be able to verify whether it lies in the correct range or to detect and identify the reasons why it may not be working properly.
A pressure gauge is the instrument used for measuring fluid pressures in both hydraulic and pneumatic circuits, and generally determines the difference in pressure between the fluid and the local pressure.
Given that most pressure gauges measure the difference between the pressure of the liquid and the local atmospheric pressure, the latter must be added to the value indicated by the pressure gauge to find the absolute pressure. A negative reading on the gauge is caused by a partial vacuum.
Pressure gauges are used to measure gauge pressures that vary between 0–1 kg/cm2 and between 0–10,000 Kg/cm2, and to measure vacuum. The gauge accuracy may be between 0.1 and 2% of full scale, depending on the material, design and precision of the parts.
Pressure gauges are usually installed on pumps, portable compressors, industrial equipment, hydraulic and pneumatic systems, instrumentation and pressurised containers, and various aspects must therefore be considered when selecting a gauge:
TYPE:
The different types of pressure gauges available come in a series of copper alloys, stainless steels and nichrome. Copper alloys give better results in some respects, but stainless steels offer greater resistance to corrosion.
Nickel iron alloys are also used. Their coefficient of expansion is very small, meaning that the pressure reading is not affected by the temperature of the instrument.
Mechanical and pneumatic instruments have an accuracy of 0.5% of the scale.
SIZE:
Hydraulic pressure gauges have diameters of 63 and 100 mm, while pneumatic gauges come in diameters of 40, 50 and 63 mm.
ASSEMBLY:
Pressure gauges can be vertical or back mounted, and can also be designed for mounting on a panel using a frontal ring or flange. Each of these details affects the selection of the ideal gauge.
CASING MATERIAL:
At Leku-Ona Global Solutions we can manufacture the pressure gauge casing in plastic, black painted steel or stainless steel. Hydraulic pressure gauges are usually filled with glycerine while pneumatic gauges are usually dry.
The face is manufactured from glass or polycarbonate and the tubular spring (inside) is brass.
Ranges or scales in hydraulic pressure gauges
Hydraulic pressure gauges have scales from 0–0.6 bar to 0–1000 bar (depending on the model), while the ranges for pneumatic gauges are 0-1 bar and 0-20 bar.
For vacuum gauges, the scales for vacuum, vacuum/pressure or pressure are usually -1-0 bar or -1-3 bar. Precision class (3-2-3%) 1 or 1.6. Manufactured in accordance with ASME / ANSI 40-1, B.1985.
Ranges to 30”Hg/6000 psi.
FITTING:
The standard threaded tube is made from brass but Leku-Ona Global Solutions also offers plastic and rustproof (on request). Standard connectors come with male fittings GAS 1/8″, 1/4″,1/2 “, depending on the model (others on request).
The gauge can be mounted to a minimex hose, tubing joint, instant fitting or valve.
Gauge protection
Pressure gauges are protected using a rubber protector or an inline mounted valve, 90º valve, with switch or panel-mounted switch.
ACCU-AIRE HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC PRESSURE GAUGES

GLYCERINE HYDRAULIC PRESSURE GAUGES

SPECIFICATIONS
STAINLESS STEEL HOUSING/BRASS INTERIOR (DRY)
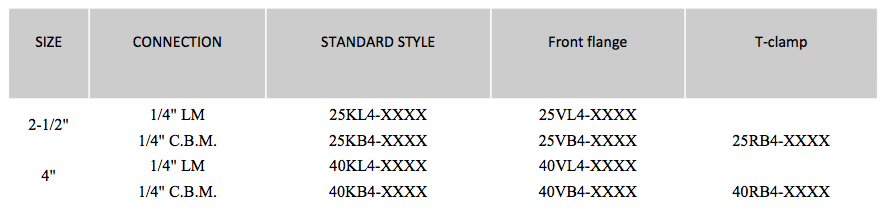
STAINLESS STEEL PRESSURE GAUGES (DRY)
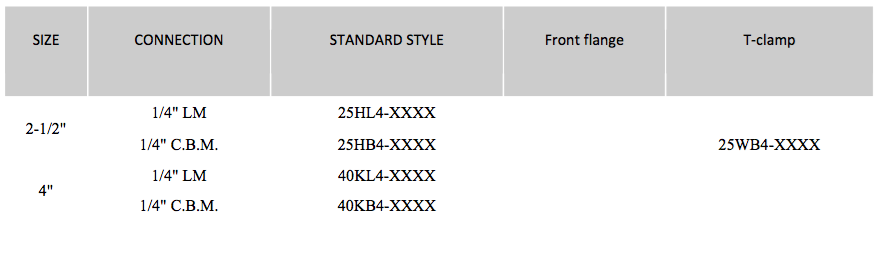
To complete the model number, add the total value of the pressure scale to identify the initial design. .
PNEUMATIC PRESSURE GAUGES (DRY)

SPECIFICATIONS
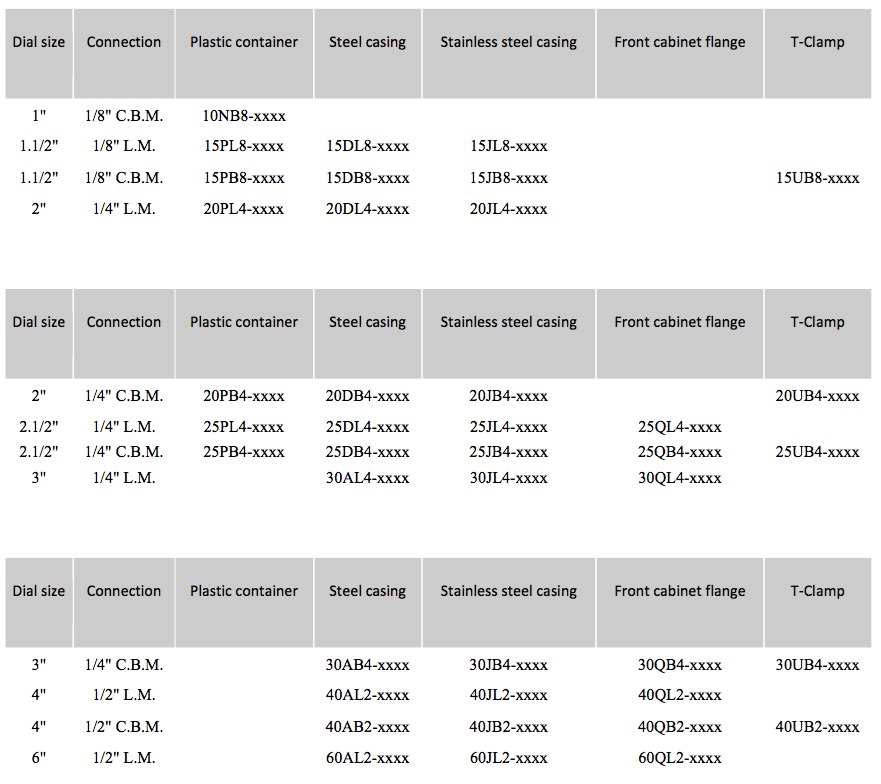
For more information on the range of ACCU-AIRE PRESSURE GAUGES available at LEKU-ONA, contact us at: | T +34 943 74 34 50 | E leku-ona@leku-ona.com







 sending...
sending...